1. What is the Internet?
📖 Notes:
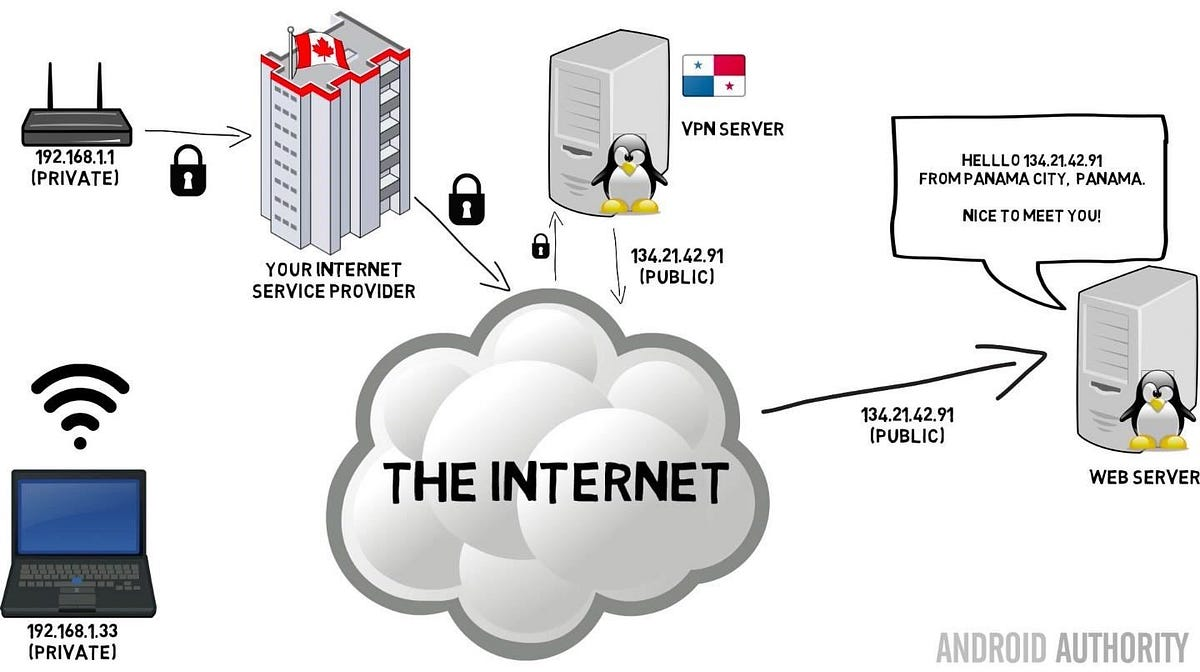
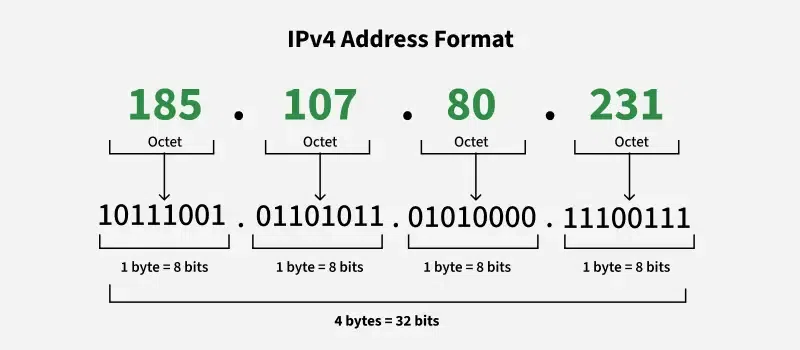
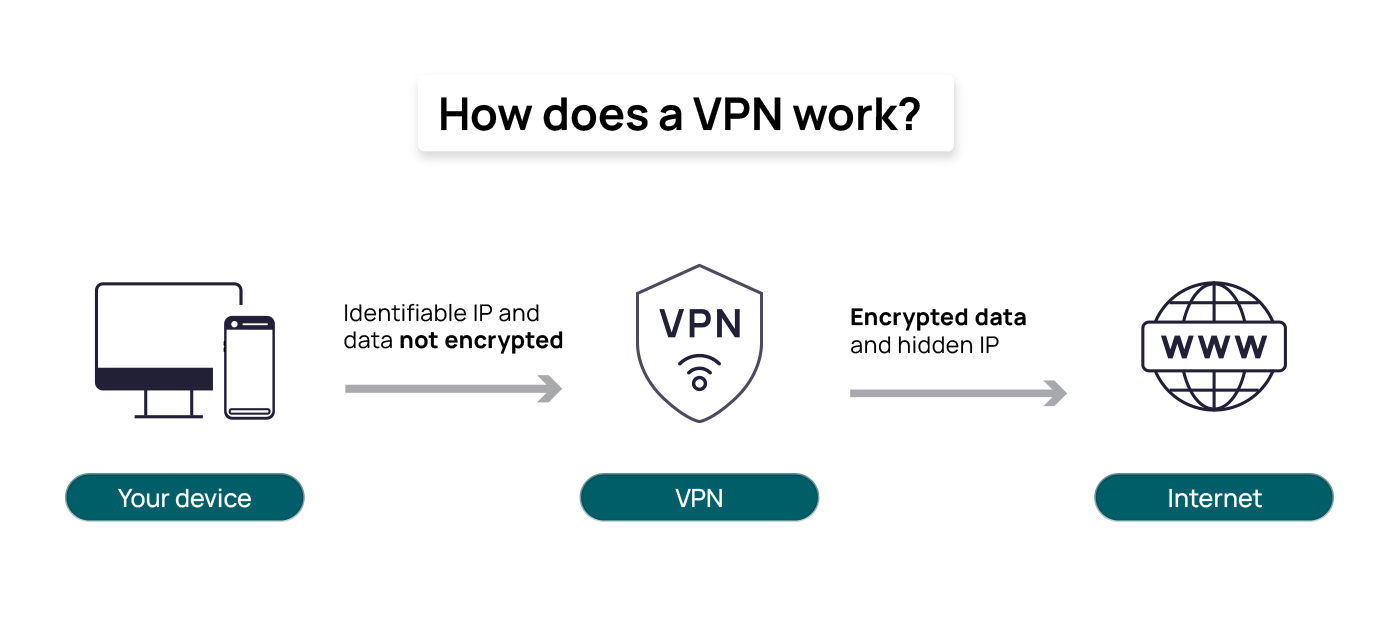
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers and devices that allows users to access and share information and devices, allowing them to communicate and exchange data. It enables users to access a wide range of services, such as websites, emails, social media, online applications, and cloud storage. Through standardized communication protocols, the Internet facilitates the sharing of information, resources, and media across vast distances, making it an essential tool for worldwide:
Education
Business
Entertainment
Personal Communication